Contents of this Section:
Overview of the Script Editor Window

The Script Editor Window is where all functions and methods can be defined, modified or removed. These functions and methods contain the client-side logic that is executed when certain user actions occur or when they are invoked by other client or host procedures. To open this window, select "View-->Script Editor" from the menu bar in the Design Window. You can also double-click a function in the "Available Functions" listbox in the design window to both open the Script Editor and position the selected function in the text editor for editing in one step.
A Function is a name assigned to a group of one or more Client or Host methods. A function can contain any number of methods, of any type, in any desired order. You can think of a function as being similar to a host procedure or subroutine, with each method being one statement in the procedure. A function can be executed as a result of any of the following actions:
The objects referenced in a Client Method may be objects in the same "app" or in any other "app" which has been opened in the Script Editor Target Tree. For example, this allows "myapp1" to open a frame in "myapp2" when a button is clicked in "myapp1" which is linked to a function containing a client method that makes the frame visible. (Note: not implemented in Version 3.0).
Host Methods are run on both the client and the host.
Control statements in the scripting language provide looping constructs, conditional statements ("If/Then/Else") and similar ways to control execution sequence, as in any true programming language.User Tip: Note that one or more of the CIOs may be message or warning boxes, which are modal objects (the user cannot do anything else in the app while a modal dialog box is displayed). If a CIO containing a message box or warning box is received, the animation will continue until the user dismisses this modal box by clicking the OK button, so that the processing of any other CIOs in the host method can be completed. After all CIOs received from the host have been processed, the host method ends and then the animation ends.
Functions are executed when they are invoked within a client function
or host procedure, or when any of the event(s) to which they are linked
take place. Functions are linked to an event of an object by associating
them in the
Events Panel of the Properties
Panel in the Design Window. For a more comprehensive discussion of
methods, objects, methods and events, see the Overview
of Functions, Methods and Events section.
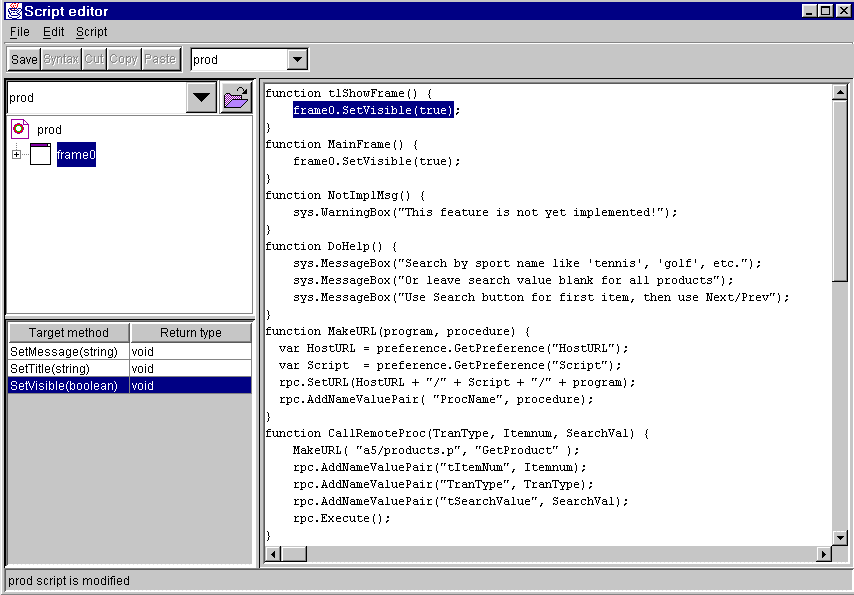
This listbox allows selection of the xml app whose script is to be edited. The "open" button to the right of the listbox allows you to open an app that has not yet been opened during this session. This listbox and button operate the same as the corresponding objects in the main Design Window.
The Target Tree is used to select the object upon which a method will operate. It works like all other trees in Jargon Writer. The target object can be any object in the currently active app, or it can be any object in any other app which is opened in the Target Tree. If you are opening another app, it must be in a directory that can be accessed in the "Open a File" dialog box which appears when the "Open" button at the top of the Target Tree is clicked.
To select a target object, open the desired app, then expand the tree until the desired object is visible, then click on that object so that it is highlighted.
The listbox below the Target Tree (lower left) shows the available methods that are valid for the component that is currently highlighted in the Target Tree. This listbox has two columns.
The first column shows the correct spelling of the method name (note that upper/lower case is significant), and the type and sequence of any required parameters. Parameter types are String, int and boolean.
The second column shows the type of value that is returned by the method when it is executed. Many methods return nothing ("void"), while others return one of the valid data types: String, int or boolean.
If a method is double-clicked, it and the selected component to which it applies will be inserted into the Text Editor panel at the point where the insertion cursor was last positioned. Also, if there was no other text on the line where the insertion was done, a concluding semicolon (";") will be added. If the method has any parameters, their type will be inserted within parentheses, and these must be replaced by the desired parameter values, as constants or methods which return a value of the correct type.
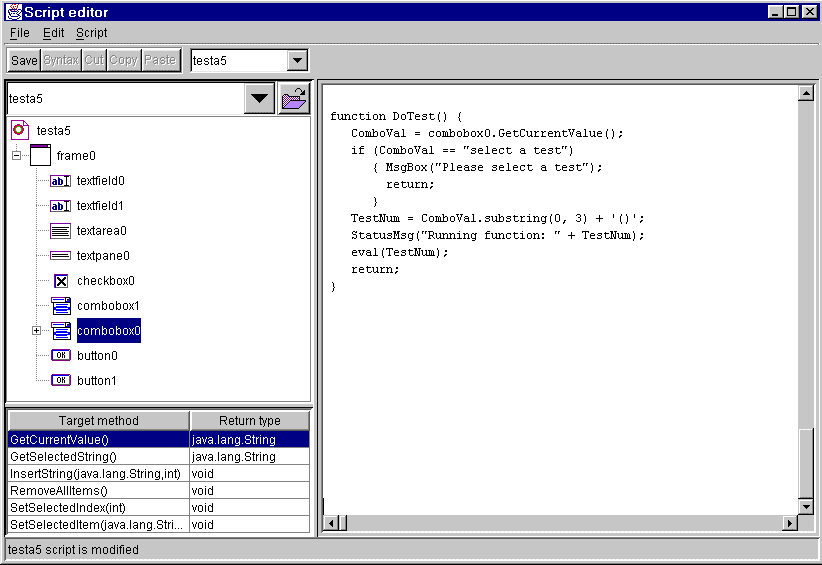
The Text Editor Panel is where functions and methods are entered and changed, using ECMAScript (similar to JavaScript). Each xml app must, at a minimum, have at least one function that contains a frame method which sets an initial frame visible. There may be any (reasonable) number of functions within an xml app, and each function may contain any number of methods and other statements such as variable definitions, looping and conditional statements, etc.
For details on these methods, functions, and other scripting language features, see the Writing Scripts and Client Methods documents. For a more general introduction to objects, methods and functions, see the next section Functions, Methods and Events.
The Status Panel at the bottom of the Script Editor Window contains a one-line message area at the lower left in which various Jargon Writer help messages are displayed during each step of working with methods. No input fields are used in the Status Panel.
<-- Previous Section Up to Top Return to Help Index Next Section -->